Table of Contents
SQL Server Error : 18456 Details
SQL Server Error: sql server error 18456
Severity: 14
Event Logged or not: Yes
Description:
Login failed for user ‘%.*ls’.%.*ls%.*ls
Severity 14 Description:
Indicates security-related errors, such as permission denied.
Details for sql server error 18456
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Product Name | SQL Server |
| Event ID | 18456 |
| Event Source | MSSQLSERVER |
| Component | SQLEngine |
| Symbolic Name | LOGON_FAILED |
| Message Text | Login failed for user ‘%.*ls’.%.*ls |
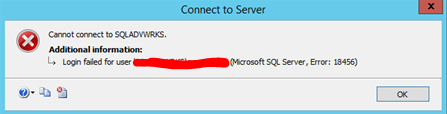
When a connection attempt is refused due to an authentication failure involving an incorrect password or user name, the client receives a message that looks like this: “User ‘user name>’ was unable to log in. (Error: 18456 in Microsoft SQL Server) “..
Related errors include:
- sql server error 18456
- error sql server 18456
- error 18456 sql server
- microsoft sql server error 18456
- sql server error number: 18456
- sql server error 18456 sql server authentication
- error number 18456 sql server
- microsoft sql server error:18456
- sql server odbc error 18456
- error 18456 sql server 2017
The following is additional information that was returned to the client:
"Login failed for user '<user_name>'. (.Net SqlClient Data Provider)"
"Server Name: <computer_name>"
"Error Number: 18456"
"Severity: 14"
"State: 1"
"Line Number: 65536"
The following message might also be returned:
"Msg 18456, Level 14, State 1, Server <computer_name>, Line 1"
"Login failed for user '<user_name>'."
Reading sql server error log location from SQL Query
Identifying SQL Server Error Log File used by SQL Server Database Engine can be done by reading SQL Server Error Logs. DBA can execute the XP_READERRORLOG extended stored procedure to read the SQL Server Error Log and search for its location used by the instance of SQL Server.
USE master
Go
xp_readerrorlog 0, 1, N'Logging SQL Server messages in file', NULL, NULL, N'asc'
Go
For other ways to read and find error log location please our artcile https://sqlserver-dba.co.uk/error-log/sql-server-identify-location-of-the-sql-server-error-log-file.html
Additional information for sql server error 18456:
In error sql server error 18456 , the information of nature of the authentication issue is purposefully hidden in the error message sent to the client to increase security. However, a comparable error for sql server error 18456 in the SQL Server error log provides an error status that corresponds to an authentication failure condition. Determine the cause of the login failure by comparing the error status to the following list for sql server error 18456.
| State | Description of error sql server 18456 |
|---|---|
| 1 | Error information is not available. This state usually means you do not have permission to receive the error details. Contact your SQL Server administrator for more information. |
| 2 | User ID is not valid. |
| 5 | User ID is not valid. |
| 6 | An attempt was made to use a Windows login name with SQL Server Authentication. |
| 7 | Login is disabled, and the password is incorrect. |
| 8 | The password is incorrect. |
| 9 | Password is not valid. |
| 11 | Login is valid, but server access failed. One possible cause of this error is when the Windows user has access to SQL Server as a member of the local administrators group, but Windows is not providing administrator credentials. To connect, start the connecting program using the Run as administrator option, and then add the Windows user to SQL Server as a specific login. |
| 12 | Login is valid login, but server access failed. |
| 18 | Password must be changed. |
| 38, 46 | Could not find database requested by user. |
| 58 | When SQL Server is set to use Windows Authentication only, and a client attempts to log in using SQL authentication. Another cause is when SIDs do not match. |
| 102 – 111 | AAD failure. |
| 122 – 124 | Failure due to empty user name or password. |
| 126 | Database requested by user does not exist. |
| 132 – 133 | AAD failure. |
Other error states also exist for error sql server 18456 and signify an unexpected internal processing error.
Also to note: In error sql server 18456 “An attempt to log in with SQL authentication was unsuccessful. Only Windows authentication is enabled on the server.” In the following circumstances, it is possible to return it.
- When the server is configured for mixed mode authentication and an ODBC connection uses the TCP protocol but does not declare that the connection should be trusted.
- When the server is configured for mixed mode authentication and an ODBC connection uses named pipes, the credentials provided by the client to open the named pipe are used to automatically impersonate the user, and the connection does not expressly state that it should use a trusted connection.
Solution for Resolving the Error sql server 18456
- Verify that SQL Server is configured in Mixed Authentication Mode if you’re trying to login using SQL Server Authentication. Change server authentication mode if need to be.
- If you’re using SQL Server Authentication, double-check that the SQL Server login exists and that you’ve spelled it correctly.
- If you’re trying to login with Windows Authentication, make sure you’re logged into the right domain.
Contact your SQL Server administrator if your problem is in state 1. - Start your application using the Run as Administrator option if you’re trying to connect with your administrator credentials. When you’re connected, create an individual login for your Windows user.
- Confirm that the login was not removed following migration to a contained database user if the Database Engine supports confined databases.
- Connections from services running under NT AUTHORITYNETWORK SERVICE must authenticate using the computer’s fully qualified domain name when connecting locally to an instance of SQL Server.
Alternate Solutions or other common troubleshooting steps
-
Restarting SQL Server Service(non production instances only), if nothing else works…
- To Restart, Start or Stop the SQL Server instance by right click on sql server instance in SSMS or in SQL. You may need to open SSMS as administrator to start, stop the instance.
-
Other ways for restarting SQL server Service
- From SQL Configuration manager from Start menu
- From Services in Windows server
- From Cmd using net start and net stop
Activity Monitor in SQL Server 2008 :
Open up Activity Monitor Using Object Explorer
In Object Explorer, right click the SQL Server 2008 Instance and click on Activity Monitor.
Also can be opened from SQL Server 2008 Management Studio’s toolbar, by clicking Activity Monitor
It shows the graphical display of Processor Time (%), Number of Waiting Tasks, Database I/O (MB/Sec) and the Number of Batch Requests/second.
For information on SQL Server Activity monitor go to https://sqlserver-dba.co.uk/sql-server-administration-basics/activity-monitor
Or using SQL Query analyzer window to run sp_who2 command which is less resource intensive and gives same information as activity monitor.
SQL Server Error Code and solution summary
SQL Server Error: sql server error 18456
Severity: 14
Event Logged or not: Yes
Description:
Login failed for user ‘%.*ls’.%.*ls%.*ls
Make sure username, password are correct.
Quick checks for error sql server 18456 is using if AD username with windows authentication then make sure account is not locked out.
Also if recently changed AD username with new password then try log off and log back in for resolving error sql server 18456.