Table of Contents
SQL Server Error : 916 Details
SQL Server Error: 916
Severity: 14
Event Logged or not: No
Description:
The server principal “%.*ls” is not able to access the database “%.*ls” under the current security context.
Severity 14 Description:
Indicates security-related errors, such as permission denied.
Accessing the SQL server database using SQL Server Management Studio with a limited number of permissions (database read or write) may result in SQL Server Error 916, with the message “The server principal username is unable to access the database database name under the current security context.”
Reason or Cause of error
The login lacks the necessary permissions to connect to the specified database. Logins that can connect to this instance of SQL Server but do not have specific permissions in a database are granted the guest user’s permissions. This is a security measure that prevents users in one database from connecting to databases in which they do not have access. This error message may appear if the guest user lacks CONNECT permission to the named database and the trustworthy property is not set. This error message may appear if the guest user lacks CONNECT permission to the specified database.
The main issue is caused by SQL Server Management Studio bugs that prevent the user from connecting to the database and refuse to display the database list. There could be a number of other causes for SQL Server Error 916.
The user is not allowed to view the data of the selected column in the database. The database is not currently accessible.
There are several columns in the list of Object Explorer Details, including Size, Space available, Data Space Used, Default file group, Index Space Used, Mail host, and Primary file path, and the user has added at least one of them.
If the database’s Auto Close option is enabled, SQL SSMS cannot retrieve the Collation column.
If a user tries to expand the database folders under a node in SQL Server 2008, even if he is not a member of a Sysadmin fixed server role or does not have the authority to access the database. Connection permission is required if the guest user wishes to expand the database nodes; otherwise, the following error message will be displayed:
Failed to retrieve data for this request (Microsoft.SqlServer.Manager.Sdk.Sfc)
In SQL Server 2005, if a guest user who is neither a member of a Sysadmin fixed server role, nor having the permissions is able to expand the database
Cannot show requested dialog.(SqlMgmt)
Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 (OCS 2007) can be affected by this issue and the services will not start even after the server is started. The following error message will be visible in the Event Viewer:
Event Type: Error
Event Source: OCS User Services
Event Category: (1006)
Event ID: 30962
Date:
Time:
User: N/A
Computer: ‘computer name’
Reading sql server error log location from SQL Query
Identifying SQL Server Error Log File used by SQL Server Database Engine can be done by reading SQL Server Error Logs. DBA can execute the XP_READERRORLOG extended stored procedure to read the SQL Server Error Log and search for its location used by the instance of SQL Server.
USE master
Go
xp_readerrorlog 0, 1, N'Logging SQL Server messages in file', NULL, NULL, N'asc'
Go
The parameters for XP_READERRRORLOG are:
1. Value of error log file we would like to read. values are 0 = current, 1 = last one before current, 2 = second last before current etc…
2. Log file type:- 1 or NULL = error log, 2 = SQL Agent log
3. Search string 1:- String one you want to search for
4. Search string 2:- String two you want to search for to further refine the results
5. start time for Search
6. end time for search
7. Sort order for search results:- N’asc’ = ascending, N’desc’ = descending
By default, we have 6 Server Error Logs kept but we can increase the number of SQL Server Error Logs from the default value of six.
For other ways to read and find error log location please our artcile https://sqlserver-dba.co.uk/error-log/sql-server-identify-location-of-the-sql-server-error-log-file.html
Solution for Resolving the Error
Grant permissions:
use msdb ;
GO
GRANT CONNECT TO [Adventure-Works\Test] ;
USE msdb ;
GO
GRANT CONNECT TO guest ;
and
ALTER DATABASE AdventureWorks SET TRUSTWORTHY ON;
We can check the granted permissions for the guest-user by using the following command (sysadmin fixed server member should run this) USE msdb; SELECT prins.name AS grantee_name, perms.* FROM sys.database_permissions AS perms JOIN sys.database_principals AS prins ON perms.grantee_principal_id = prins.principal_id WHERE prins.name = ‘guest’ AND perms.permission_name = ‘CONNECT’; GO
When the above command is executed, the user is presented with a table containing all of the guest user’s attributes.
An empty result, on the other hand, indicates that the guest user has been disabled in the database, and the SQL Server error 916 will be displayed once more. You can correct the error by implementing one of the available solutions.
1. The user can use the following solutions to resolve the error when accessing the database. Any of them will assist you.
- In the SSMS, go to the View section and select Object Explorer Details.
- Deselect Collation by right-clicking on Column Header.
- Refresh the server and operate a database.
2. From the SSMS menu, select View > Object Explorer details.
Click the Database folder in the Object Explorer window.
Select Reset View from the menu that appears when you right-click on the column header.
Refresh the Database folder to complete the final step.
3. Check the database’s Auto Close setting, set it to False, and continue.
The solutions described above may resolve the issue, allowing the user to continue with the workflow.
Alternate Solutions
-
Restarting SQL Server Service(non production instances only)
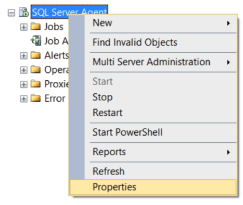
- To Restart, Start or Stop the SQL Server instance by right click on sql server instance in SSMS or in SQL. You may need to open SSMS as administrator to start, stop the instance.
-
Other ways for restarting SQL server Service
- From SQL Configuration manager from Start menu
- From Services in Windows server
- From Cmd using net start and net stop
2.Checking SQL Performance metrics like CPU, Memory
Check SQL Server CPU, Memory usage, longest running queries, deadlocks etc.. using activity monitor or sp_who2.
To view Activity Monitor in SQL Server 2005 and in SQL Server 2008, a user must have VIEW SERVER STATE permission.
2 Different Ways to Open up Activity Monitor in SQL Server 2008 are mentioned below:
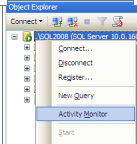
Open up Activity Monitor Using Object Explorer
In Object Explorer, right click the SQL Server 2008 Instance and click on Activity Monitor.
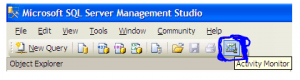
Also can be opened from SQL Server 2008 Management Studio’s toolbar, by clicking Activity Monitor
SQL Server Error Code and solution summary
SQL Server Error: 916
Severity: 14
Event Logged or not: No
Description:
The server principal “%.*ls” is not able to access the database “%.*ls” under the current security context.
With the help of this page, a person can learn about SQL Server error 916, the problems that occur as a result of it, and the causes. As a result, a user can obtain detailed information about the SQL server as well as the possible error message displayed if the guest user wishes to expand the database node in order to view its data.